Sustainability
AI energy dilemma: data centers, grid expansion, efficiency
The AI energy dilemma: data centers, grid expansion and efficiency
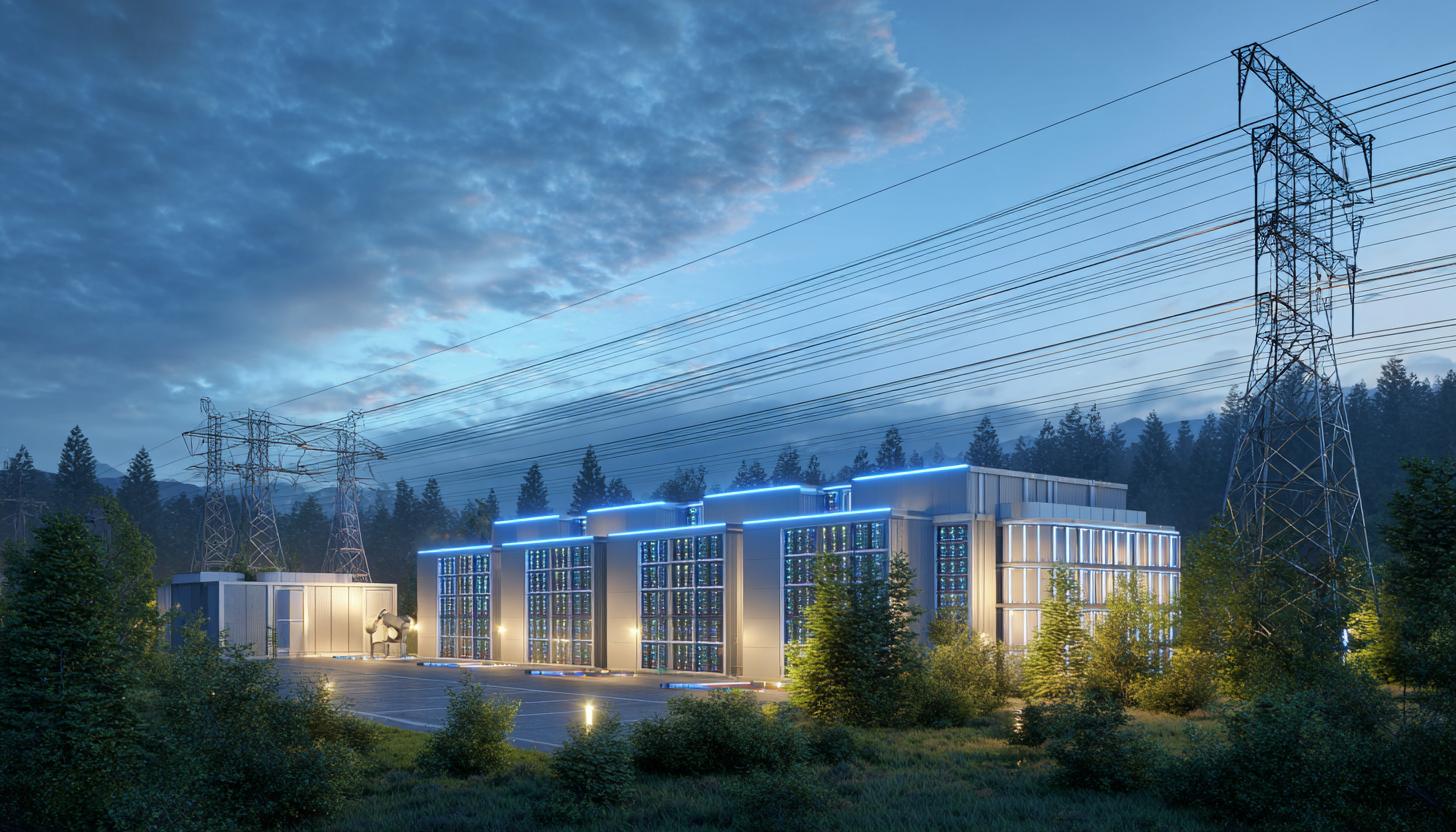
In 2025, companies and political decision-makers alike will be faced with an urgent challenge: how can the increasing energy consumption of AI data centers be reconciled with sustainability, infrastructure and cost-effectiveness? With the rapid spread of AI-supported applications in all areas – from automation and data analytics to large language models – energy consumption is exploding worldwide. This raises fundamental questions about scalability, efficiency and infrastructure measures.
For companies in the technology sector in particular – including distributors and integrators of mobile devices, business IT solutions and infrastructure components – this change offers not only challenges, but also enormous opportunities to position themselves flexibly and sustainably with customized hardware. In this article, we examine the AI data center energy dilemma in detail, highlight current developments and evaluate how companies can prepare themselves technologically and organizationally.
Current status quo: hunger for energy meets drive for innovation
The use of artificial intelligence has multiplied in recent years – particularly through large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4, Mistral or Gemini, but also through specialized ML-based business applications in production, logistics or customer service. These systems require immense computing power – not only for training, but also for later use (inference).
As a result, companies are increasingly reliant on the flexible rental of powerful computers in order to access the computing power they need at short notice.
This trend is leading to a drastic increase in energy requirements. Large hyperscalers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure alone now consume more electricity than entire branches of industry in smaller countries.
AI data center energy consumption: facts and figures
| Criterion | 2023 | Forecast 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Global electricity consumption by data centers | approx. 460 TWh | over 800 TWh |
| Percentage share of global electricity consumption | ~2% | ~4% |
| Power consumption through AI models (training & inference) | Difficult to measure, but already significant | Expected to double to quintuple (depending on the model) |
| Number of large hyperscaler data centers worldwide | approx. 800 | over 1,200 (planned by 2025) |
Particularly problematic: the efficiency gains in cloud services can no longer compensate for the absolute energy consumption due to massive scaling. AI applications often run on specialized chips such as GPUs or TPUs, which have a much higher energy requirement per computing operation than conventional CPUs.
The energy challenge for companies
Companies, especially in the B2B sector, are facing a dilemma today: on the one hand, they need to use AI technologies in order to remain competitive. On the other hand, the integration of energy-hungry AI systems requires massive investments in computing power, infrastructure and cooling.
One way to meet such requirements, even at short notice and on a project-specific basis, is to rent laptops with special AI functionality on demand as the computing load increases.
- Scalability: Local infrastructures quickly reach their capacity and cooling limits
- Grid expansion: High energy demand puts a strain on the electricity grid; regional blackouts can occur during peak loads
- Security: More data centers mean more potential points of attack
- Sustainability: CSR requirements and ESG standards oblige companies to use climate-friendly technologies
Answers to the dilemma: technological options and strategies
The solution does not lie in doing without, but in smarter technology and strategic flexibility. Mobile, scalable device solutions and temporary computing clusters in particular are becoming a viable alternative for many companies.
Increased efficiency through modern hardware
Current developments enable significantly higher computing power per watt. Special chips such as NVIDIA Grace Hopper or AMD Instinct offer extremely high ML power with significantly improved energy efficiency. Modern notebooks and workstations with AI accelerators also integrate these chips on the client side. If you are looking for maximum mobility with strong AI performance, the OMEN Transcend laptop is a powerful choice for demanding deep learning tasks.
The HP OmniBook Ultra laptop, which combines performance and energy efficiency for professional applications, is particularly suitable for the office.
The use of modular, rentable solutions is therefore being considered at company level. Mobile devices with GPU/AI support offer a flexible alternative to an in-house data center, especially when high computing power is required at short notice (e.g. for training courses, AI projects or events). 2-in-1 solutions such as the HP Spectre x360 2-in-1 laptop also enable flexible deployment scenarios for creative and analytical work with artificial intelligence.
On-demand rental instead of investment backlog
Building your own AI hardware is expensive and time-consuming. Our solution: Tailor-made rental packages with state-of-the-art AI capability that are available at short notice. Advantages:
- No more investment risk – you only pay for what you actually use
- Always up to date: access to the latest hardware generation
- Support with roll-outs, test runs or prototyping
- Can be combined with mobile devices incl. remote management
In the gaming and workstation environment, it makes sense to temporarily rent a dedicated gaming desktop with a powerful GPU for computing-intensive AI applications if maximum performance is required at short notice.
Especially in AI-driven areas such as predictive maintenance, smart analytics and edge AI, rental solutions are a game changer for companies.
Grid expansion – a national challenge that shapes the economy
The increasing demand for electrical energy is causing bottlenecks across all sectors. According to a study by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy, Germany will need to add more than 30 gigawatts by 2030 for digital and data center infrastructure alone – roughly the same amount as 20 nuclear power plants.
This also means that anyone investing in power-hungry AI infrastructure today must expect delays or tariff increases. Companies that can organize their computing power via mobile, distributed and temporary solutions (“edge + rental clusters”) partially circumvent this problem – for example, through the flexible use of notebooks such as the HP Dragonfly G4 for on the go and in the office.
Practical example: Mobile device rental for an AI training project
An international automotive supplier wanted to train 100 developers and data analysts on a new AI model within three months. In-house infrastructure was not sufficient and cloud scaling was too expensive.
Our solution:
- Provision of 120 high-performance workstations with NVIDIA RTX 4090 & AI-enabled software
- Central control via remote device management system and preconfigured software environment
- Withdrawal after project completion incl. GDPR-compliant data deletion
The result: optimum performance without permanently tied-up infrastructure or investment costs – and full flexibility thanks to rental hardware.
Where is the journey heading? Trends for 2025 and beyond
The following developments are clearly emerging and should be taken into account in the planning of technology managers:
- Green AI: Research and politics are pushing AI solutions that work much more economically with comparable performance. Models such as small language models (SLMs) or quantized networks are conquering the market.
- Edge AI: More and more computing power is moving from the cloud to the edge network – smaller devices take over decisions locally, which drastically reduces data traffic. With suitable rental laptops for Edge AI, such infrastructures can be flexibly mapped.
- Temporary computing power: “Infrastructure on demand” is becoming the norm. Particularly popular: rental packages with optional GPU support and AI optimization.
FAQ: Frequently asked questions about “AI data center energy consumption”
How much energy does an AI model consume on average?
This depends heavily on the size and application – training a model such as GPT-4 can take several megawatt hours (MWh). Inference processes on thousands of endpoints also add up quickly. With scalable rental solutions, energy requirements remain more predictable and controllable.
Is cloud AI really more efficient?
Yes and no. Although central data centers are very efficient, this effect is relativized with high usage intensity and large models. Particularly price-sensitive: effectively distributing the computing load between edge, cloud and dedicated devices.
What rental solutions are available for AI end devices?
We offer flexible rental packages for AI-enabled laptops, workstations, tablets and mobile devices – also with pre-installation of the most common ML frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch and ONNX. For high mobility and performance, we recommend models such as the OMEN Transcend laptop or the HP OmniBook Ultra.
How sustainable is the use of mobile devices with AI support?
Well-designed rental solutions have a significantly smaller ecological footprint than permanent in-house purchases. In addition, professional recycling and lifecycle management have a targeted resource conservation effect. Rely on sustainable computer rental for your next AI project.
Conclusion: finding a balance in the energy-AI paradox
The energy dilemma surrounding AI data centers is real – but it can also be solved. Companies that focus on efficient technologies, smart rental instead of purchase and hybrid infrastructures at an early stage will not only remain competitive, but also sustainable.
On our website you will find customized products and mobile AI solutions – ideal for your projects in the fast, digital world of 2025. Check our current notebook rental offers for AI applications directly or let us advise you individually!
Enquire now and secure a consultation appointment!
Read more - You may also be interested in
Would you like to delve deeper into the topic or discover similar content? Below, we have compiled three additional articles for you that are thematically related to this article. These may also be relevant and interesting for your company.